Nutritional Profile of Great Northern Beans

Nutrition facts great northern beans – Great Northern beans are a nutritional powerhouse, offering a remarkable blend of macronutrients and micronutrients that contribute significantly to a balanced diet. Their versatility in culinary applications, from hearty soups to vibrant salads, makes them an excellent addition to a healthy eating plan. Let’s delve into the detailed nutritional composition of this humble yet impressive legume.
Macronutrient Composition of Great Northern Beans
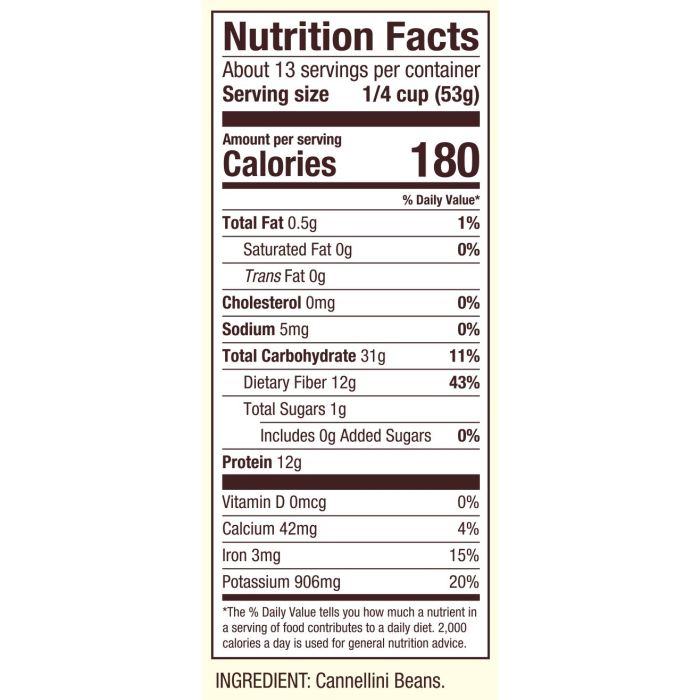
A one-cup serving (approximately 179 grams) of cooked Great Northern beans provides a substantial amount of macronutrients. These beans are particularly rich in protein and carbohydrates, making them an ideal source of sustained energy. The precise values can vary slightly depending on factors such as growing conditions and cooking methods, but a typical serving offers approximately 15 grams of protein (contributing about 30% of the recommended daily intake for an average adult), 45 grams of carbohydrates (around 15% of the daily value), and a modest 1 gram of fat (less than 2% of the daily value).
The high carbohydrate content is largely composed of complex carbohydrates, providing a slow release of energy and contributing to feelings of fullness and satiety.
Micronutrient Content of Great Northern Beans, Nutrition facts great northern beans
Great Northern beans are also an excellent source of various essential micronutrients, vital for numerous bodily functions. The following table summarizes the key vitamins and minerals present in a one-cup serving:
| Nutrient | Amount per 1-cup serving | % Daily Value | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Folate | 171 mcg | 43% | Essential for cell growth and development, crucial during pregnancy. |
| Thiamin (Vitamin B1) | 0.3 mg | 20% | Supports energy metabolism and nerve function. |
| Iron | 3.6 mg | 20% | Plays a crucial role in oxygen transport and red blood cell production. |
| Potassium | 700 mg | 20% | Important for maintaining healthy blood pressure and fluid balance. |
| Magnesium | 73 mg | 17% | Contributes to bone health, muscle function, and blood sugar control. |
Note: Daily value percentages are based on a 2,000-calorie diet. Individual needs may vary.
Great northern beans are a nutritional powerhouse, boasting high fiber and protein content. For a different carbohydrate source, you might compare their nutritional profile to that of a grain-based product, such as checking out the multigrain bagel nutrition facts to see the differences in macronutrients. Ultimately, both contribute to a balanced diet, but in distinct ways, highlighting the importance of dietary diversity when considering nutrition facts great northern beans.
Fiber Content and Health Benefits of Great Northern Beans
The significant fiber content of Great Northern beans is a key contributor to their numerous health benefits. These beans contain both soluble and insoluble fiber. Soluble fiber, which dissolves in water, helps regulate blood sugar levels and lower cholesterol. Insoluble fiber, on the other hand, adds bulk to the stool, promoting regularity and preventing constipation. A one-cup serving of cooked Great Northern beans provides approximately 12 grams of fiber, representing a substantial portion of the recommended daily intake.
The combined action of soluble and insoluble fiber contributes to improved digestive health, weight management, and reduced risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and type 2 diabetes. For example, studies have shown that diets rich in fiber, such as those including beans, can significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular events.
Great Northern Beans in a Healthy Diet
Great Northern beans are a nutritional powerhouse, seamlessly integrating into a balanced diet to promote overall health and well-being. Their versatility in the kitchen, coupled with their impressive nutrient profile, makes them a valuable addition to any healthy eating plan. They offer a significant contribution to dietary fiber, protein, and essential minerals, supporting various bodily functions and contributing to a feeling of sustained energy.Great Northern beans are a versatile and healthy addition to a balanced diet.
Their high fiber content aids digestion and promotes gut health, while their protein provides essential building blocks for the body. The beans’ rich mineral content, including iron and potassium, further enhances their nutritional value. Regular consumption can contribute to weight management, improved blood sugar control, and reduced risk of certain chronic diseases.
Sample Meal Plan Incorporating Great Northern Beans
The following meal plan showcases the adaptability of Great Northern beans across various culinary applications. These examples demonstrate how easily they can be incorporated into everyday meals without sacrificing taste or convenience.
- Breakfast: Savory Great Northern Bean and Spinach Frittata. This hearty breakfast combines the protein and fiber of the beans with the vitamins and minerals of spinach, creating a nutritious and satisfying start to the day. The frittata can be prepared in advance, making it a convenient option for busy mornings.
- Lunch: Great Northern Bean and Vegetable Salad with a Lemon Vinaigrette. This light yet filling salad provides a refreshing and healthy lunch option. The beans add a creamy texture and substantial protein, complemented by the crunch of fresh vegetables and the zesty flavor of the lemon vinaigrette.
- Dinner: Hearty Great Northern Bean Stew with Root Vegetables and Herbs. This warm and comforting stew is perfect for cooler evenings. The beans provide heartiness and nutritional value, while the root vegetables and herbs add depth of flavor and a range of vitamins and minerals.
- Snack: Spiced Great Northern Bean Dip with Whole-Wheat Pita Bread. This simple snack is both delicious and nutritious. The dip offers a healthy source of protein and fiber, making it a satisfying alternative to less healthy snack options. The whole-wheat pita bread adds extra fiber to this healthy snack.
Nutritional Comparison of Great Northern Beans with Other Legumes
Understanding the nutritional differences between various legumes can help in making informed dietary choices. The table below compares the protein, fiber, and iron content of Great Northern beans with kidney beans, lentils, and chickpeas, per 100g serving. These values are approximate and can vary slightly depending on the specific variety and growing conditions.
| Legume | Protein (g) | Fiber (g) | Iron (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Great Northern Beans | 21 | 15 | 6.0 |
| Kidney Beans | 21 | 16 | 6.5 |
| Lentils | 26 | 15 | 7.0 |
| Chickpeas | 19 | 12 | 4.5 |
Potential Drawbacks and Considerations

While Great Northern beans offer a wealth of nutritional benefits, it’s crucial to acknowledge potential drawbacks and understand how to mitigate them. Like many legumes, they contain compounds that can cause digestive discomfort for some individuals. Careful preparation and mindful consumption can help minimize these issues and allow you to fully enjoy the health advantages of this versatile bean.Great Northern beans, like other legumes, contain raffinose and stachyose, complex sugars that our bodies have difficulty digesting.
These sugars travel to the large intestine where gut bacteria ferment them, producing gas as a byproduct. This fermentation process can lead to common digestive side effects such as bloating, gas, and flatulence. The severity of these symptoms varies greatly from person to person, depending on individual gut microbiome composition and tolerance levels.
Digestive Discomfort and Mitigation Strategies
The most frequently reported drawback of consuming Great Northern beans is digestive discomfort. This is primarily due to the presence of oligosaccharides, which are poorly absorbed in the small intestine. To reduce gas and bloating, consider soaking the beans overnight before cooking. Soaking helps break down some of these complex sugars, making them easier to digest. Another helpful strategy is to incorporate Great Northern beans gradually into your diet, allowing your body to adjust to their presence.
Starting with small portions and gradually increasing the quantity over time can significantly reduce the likelihood of digestive upset. Furthermore, slow cooking methods, such as simmering, further enhance digestibility. Finally, incorporating digestive enzymes, such as Beano, which helps break down oligosaccharides, might be beneficial for those particularly sensitive to these compounds.
Potential Interactions with Medications and Health Conditions
While generally safe for consumption, Great Northern beans may interact with certain medications or health conditions. For instance, individuals with kidney disease should monitor their potassium intake, as Great Northern beans are a good source of this mineral. High potassium levels can be problematic for those with impaired kidney function. Furthermore, Great Northern beans, like other legumes, contain phytic acid, which can interfere with the absorption of certain minerals, such as iron and zinc.
This interaction is usually not significant for healthy individuals with a varied diet, but it’s something to consider for those with deficiencies or on specific medications. Always consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before making significant dietary changes, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions or are taking medications.
Infographic: Great Northern Beans – Benefits and Drawbacks
The infographic would be visually appealing, using a split design. One half would be vibrant green, depicting the benefits, while the other half would be a softer, muted green, highlighting potential drawbacks. Left Side (Benefits – Vibrant Green):* Top: Large, bold title: “Great Northern Beans: Nutritional Powerhouse!”
Middle
A stylized bean sprout growing upward.
Sections below the sprout, each with a small icon (e.g., a heart for fiber, a muscle for protein)
High in Fiber
Promotes digestive health and regularity.
Excellent Source of Protein
Supports muscle growth and repair.
Rich in Iron
Essential for oxygen transport and energy production.
Good Source of Folate
Crucial for cell growth and development.
Packed with Potassium
Supports healthy blood pressure. Right Side (Drawbacks – Muted Green):* Top: Large, bold title: “Potential Considerations”
Middle
A stylized bean with a small, slightly exaggerated gas bubble rising from it.
Sections below the bean, each with a small icon (e.g., a stomach with an X for bloating)
May Cause Gas and Bloating
Due to oligosaccharides.
Potential Interaction with Medications
Consult a healthcare professional.
High Potassium Content
Monitor intake if you have kidney issues.
Phytic Acid
May slightly reduce mineral absorption.The infographic would conclude with a small section emphasizing the importance of moderation and incorporating Great Northern beans into a balanced diet for optimal health benefits. The overall aesthetic would be clean, modern, and easy to understand, using clear fonts and concise language.
Top FAQs: Nutrition Facts Great Northern Beans
Are Great Northern beans good for weight loss?
Totally! They’re high in fiber and protein, keeping you full and satisfied, which can help with weight management.
Can I eat Great Northern beans every day?
Yeah, but maybe mix it up a bit! Variety is key for a balanced diet. Too many beans every day
-could* lead to some digestive issues for some people.
What if I’m allergic to beans?
Yikes! If you have a bean allergy, obviously, skip these. Check with your doctor or allergist if you’re unsure.
Are canned Great Northern beans as healthy as dried?
Dried are usually better, but canned are a convenient option in a pinch. Just be mindful of the sodium content in canned beans.