Health Benefits and Risks of Ribeye Consumption: Nutrition Facts 8 Oz Ribeye Steak
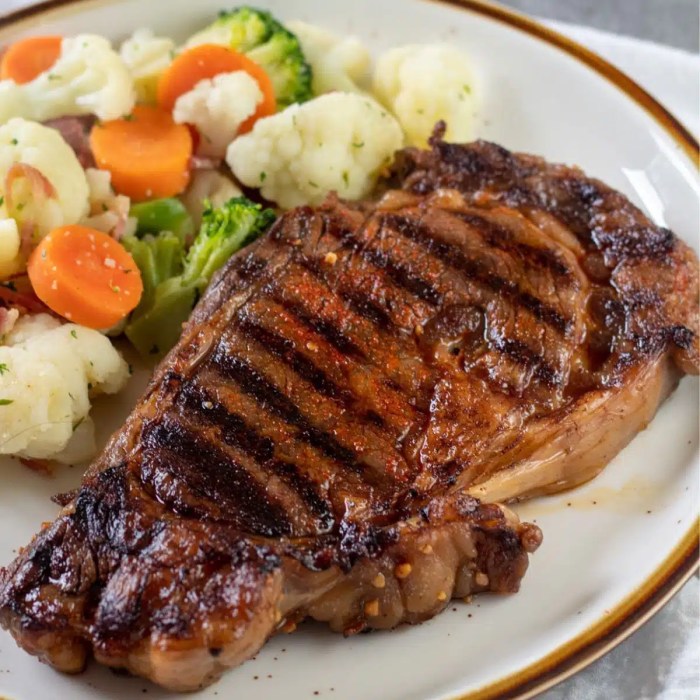

Nutrition facts 8 oz ribeye steak – Ribeye steak, a culinary favorite known for its rich marbling and intense flavor, presents a complex nutritional profile. Understanding both the potential benefits and risks associated with its consumption is crucial for making informed dietary choices. This exploration will delve into the specific nutrients found in ribeye and their impact on health, as well as address the concerns surrounding its high fat content.Ribeye steak offers a significant source of high-quality protein, essential for building and repairing tissues, supporting immune function, and maintaining overall bodily processes.
It’s also a good source of iron, crucial for red blood cell production and oxygen transport throughout the body. Furthermore, ribeye contains several B vitamins, including B12, which plays a vital role in nerve function and DNA synthesis. These nutrients contribute to overall health and well-being, provided consumption is part of a balanced diet.
Nutritional Benefits of Ribeye Steak
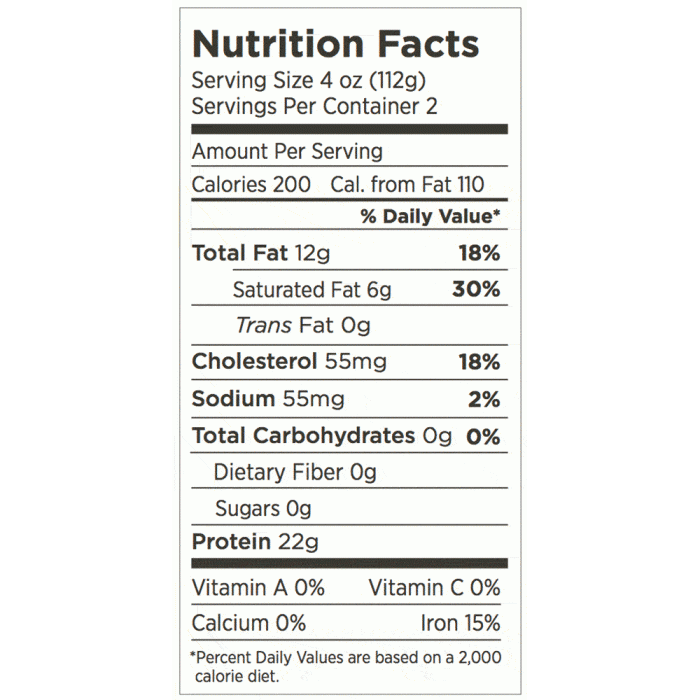
Ribeye steak provides a concentrated dose of essential nutrients. The protein content is particularly noteworthy, offering approximately 20-25 grams per 3-ounce serving, contributing significantly to daily protein needs. The iron content aids in preventing anemia, while the B vitamins support various metabolic processes. These benefits, however, must be weighed against the potential risks associated with its fat content.
Risks Associated with High Saturated Fat and Cholesterol
Regular consumption of ribeye steak, due to its high saturated fat and cholesterol content, can pose health risks. Saturated fat contributes to elevated LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke. High cholesterol levels can lead to the buildup of plaque in arteries, narrowing them and reducing blood flow. This can manifest in various cardiovascular issues, underscoring the importance of mindful consumption.
An 8 oz ribeye steak packs a hefty protein punch, but its saturated fat content is considerable. Comparing this to the nutritional profile of other popular beverages is insightful; for instance, check the mtn dew zero nutrition facts to see the stark contrast in sugar and calorie content. Ultimately, understanding the nutritional breakdown of both the ribeye and the soda helps make informed dietary choices.
For instance, individuals with a pre-existing family history of heart disease should exercise particular caution. The high cholesterol levels in ribeye are a major contributing factor to these risks.
Moderation and Portion Control in a Balanced Diet, Nutrition facts 8 oz ribeye steak
Incorporating ribeye steak into a balanced diet requires careful consideration of portion size and frequency of consumption. Moderation is key to mitigating the risks associated with its high fat and cholesterol content. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help offset the negative impacts of high saturated fat intake. Limiting ribeye consumption to occasional meals and opting for leaner cuts of beef when possible can further reduce potential health risks.
For example, choosing a 3-ounce serving instead of a larger portion can significantly decrease the overall fat and cholesterol intake. A balanced approach ensures the enjoyment of ribeye’s nutritional benefits without compromising overall health.
Ribeye Steak in Different Diets
Let’s explore how this delicious cut of beef fits into various popular dietary approaches. Understanding its macronutrient profile is key to incorporating it responsibly and effectively into your chosen eating plan. Remember, moderation and balance are crucial, regardless of your dietary preferences.
The nutritional composition of an 8-ounce ribeye steak is relatively consistent, but its place within different diets varies greatly due to the differing macronutrient ratios emphasized by each approach. We’ll examine how to integrate a ribeye strategically, ensuring it complements rather than conflicts with your dietary goals.
Macronutrient Comparison Across Diets
The following table illustrates how the macronutrient profile of an 8-ounce ribeye steak aligns with the principles of several popular diets. Note that these are approximate values and can vary based on the specific cut and preparation method. It’s crucial to consider your individual caloric needs and overall dietary intake.
| Diet | Protein (grams) | Fat (grams) | Carbohydrates (grams) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ketogenic | ~50 | ~60 | ~0 |
| Paleo | ~50 | ~60 | ~0 |
| Mediterranean | ~50 | ~60 | ~5 (from potential added vegetables) |
| Standard American Diet (SAD) | ~50 | ~60 | ~10-20 (depending on accompaniments) |
Considerations for Individuals with Specific Dietary Restrictions
While a ribeye steak can be a part of a healthy diet for many, individuals with certain health conditions or dietary restrictions need to exercise caution. Careful planning and mindful consumption are essential.
For example, individuals with high cholesterol or heart disease should limit their intake of saturated fat. Ribeye steak is relatively high in saturated fat, so moderation is crucial. Consulting a doctor or registered dietitian is recommended to determine appropriate portion sizes and frequency of consumption. Choosing leaner cuts of beef or preparing the ribeye in ways that minimize fat content can also help.
Guidelines for Preparing a Healthy and Balanced Meal with Ribeye Steak
To ensure a nutritious and balanced meal that includes an 8-ounce ribeye steak, consider the following guidelines:
Prioritize lean protein sources and healthy fats. Pair your ribeye with a generous serving of non-starchy vegetables such as broccoli, asparagus, or green beans. These add essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber, counterbalancing the fat content of the steak. A small portion of healthy fats, such as avocado or a drizzle of olive oil, can further enhance flavor and nutrient absorption.
Avoid excessive added salt and saturated fats during cooking. Grilling, baking, or pan-searing with minimal added oil are healthier cooking methods compared to deep frying.
Essential FAQs
Can I eat ribeye steak every day?
While ribeye is delicious, daily consumption isn’t recommended due to its high saturated fat content. Moderation is key for optimal health.
How does grilling affect the nutritional content of a ribeye?
Grilling can slightly reduce some nutrients due to heat, but the overall nutritional profile remains largely unchanged.
Is ribeye steak suitable for weight loss diets?
It can be, but portion control is crucial. Choose leaner cuts and incorporate it into a calorie-controlled diet plan.
What are some healthy ways to prepare a ribeye steak?
Grilling, broiling, or pan-searing with minimal added fat are healthy cooking methods. Avoid deep frying.